Although automobiles are called a kind of ground vehicle, actually they are traveling totally imersed in a fluid, the air. This is the reason for all issues related to downforce, lifting and noise. Any vehicle leaves a wake behind when traveling. In automobiles this is very similar to a blunt body. Considering the energy balance:
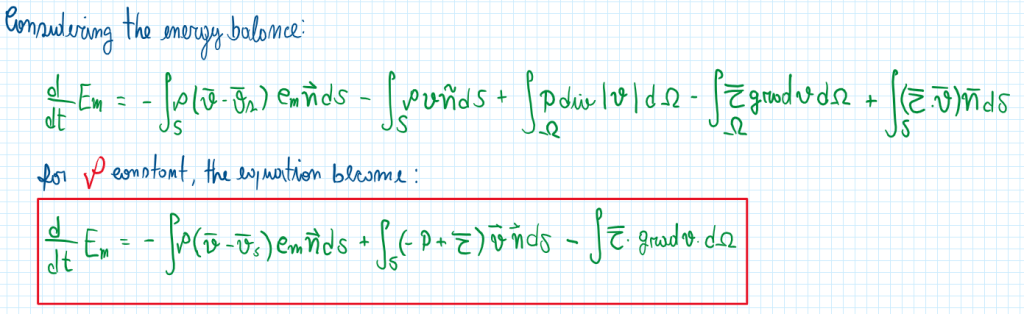
The situation of a vehicle inside a control volume can be used to analyze the energy gerated by a blunt body. The car is traveling inside of a control volume and the air far from the car is not affected by its disturbance. Understanding that one of the terms of the macroscopic balance is a difference between the velocity of the fluid and surfaces of the car, it can be seen that:
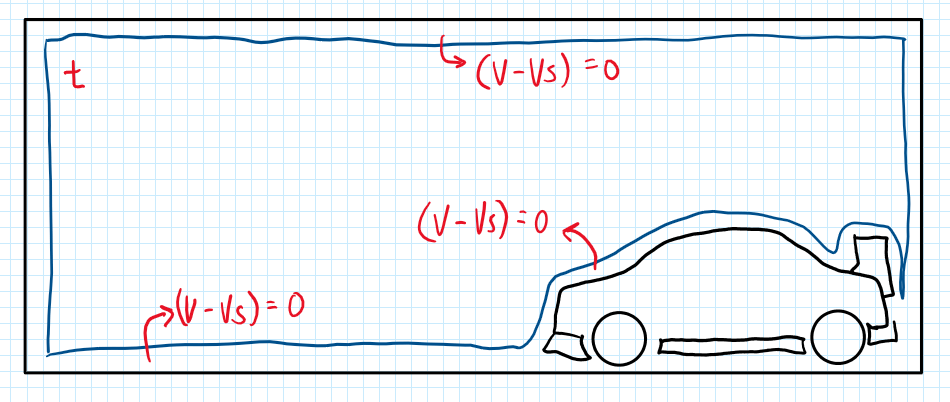
The term (V-VS) is zero everywhere, because the boundaries far from the vehicle the perturbation does not affect the flow. In addition, at the ground (V-VS) is also because there is no motion near to the surface. However, at the car surface there are velocities due to the non-slip conditions, thus (V-VS) will be also zero, because the velocity of the fluid equals to the one of the vehicle. Therefore the macroscopic energy balance can be upated:
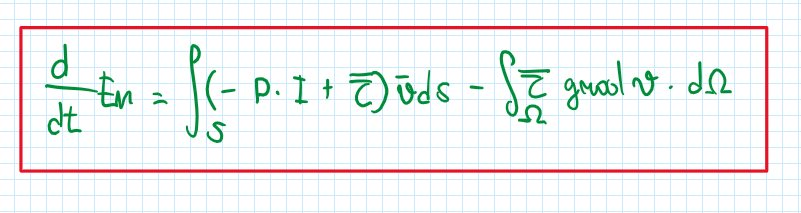
Moreover, considering that the viscous losses are small enough to be neglected, the effects in terms of energy can be demonstrated by the following graph and the macroscopic energy balance equation:
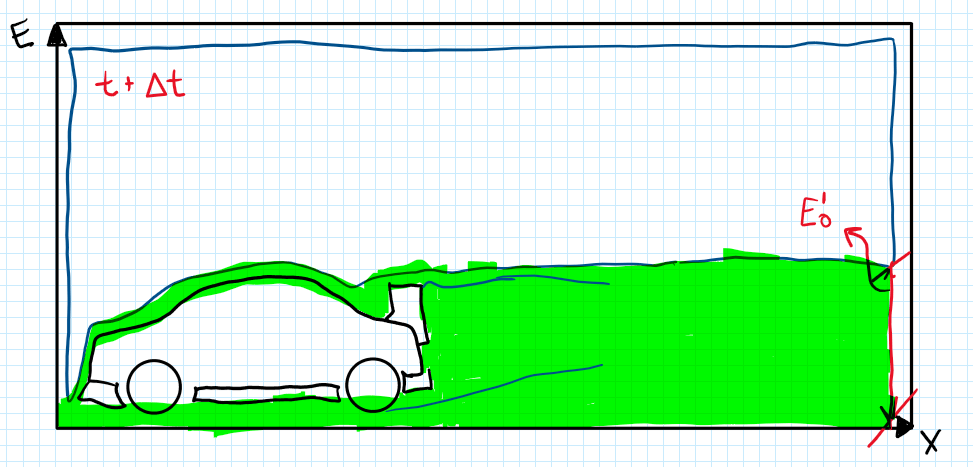
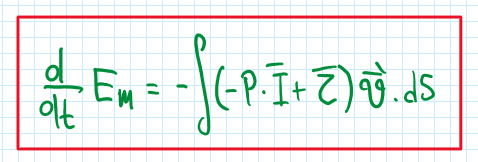
The effect of the passage of the car on these conditions is the constant wake formed behind it. The energy content is the area behind the curve, or the time differential of the energy Em. Comparing with the previous graph of the vehicle at the time moment t, the delta of Em will be the difference between the areas below the curves. In addition the magnitude of the energy content is the same for both cases, the difference is the integral (in red square):

Please note that the integral input is in Joule per meter, but deliver a result in Joule. However, the energy produced during a wake by:

After some manipulations it is possible to define that, the energy content generated by the is equal to the drag energy generated by the disturbance created. Therefore, the primary conclusion respect to these calculations is, the amount drag will require more energy by the car. The assumption of the viscous losses negligible is not real, but it helps to understand that a wake is the energy that the car must produce to overcome the drag. This energy cames from the engine.
